MICROMOTORE DENTALE E MANIPOLO DEL MICROMOTORE
DENTAL MICROMOTOR AND MICROMOTOR HANDPIECE
Luca Martinelli
Pubblicazione del 23.10.2022
Luca Martinelli
Publication of 23.10.2022
1.PREMESSA
Molto spesso con il termine micromotore viene erroneamente individuato l’insieme costituito dall’assemblato Manipolo-micromotore.
In questa scheda vedremo la differenza fra micromotore e manipolo.
1. INTRODUCTION
Very often the term micromotor is mistakenly identified as the set consisting of the handpiece-micromotor assembly.
In this sheet we will see the difference between micromotor and handpiece.
2.TERMINI E DEFINIZIONI
La norma EN ISO 1942:2020 “Dentistry – Vocabulary” definisce:
-Micromotore (micromotor): piccolo motore utilizzato per alimentare manipoli dentali tramite collegamento diretto;
-Manipolo dentale (dental handpiece): strumento con impugnatura utilizzato in odontoiatria per l'uso nel trattamento del paziente;
-Turbina ad aria o rotore ad aria (air turbin): rotore pneumatico ad alta velocità utilizzato come unità propulsiva di un manipolo odontoiatrico. Di fatto è anch’essa un manipolo solo che anziché funzionare per rapporto meccanico funziona attraverso un flusso di aria. La definizione di fresa aiuta a comprendere definitivamente la funzione del manipolo:
-Fresa (Bur): strumento di taglio rotante composto da testa, collo e gambo, progettato per adattarsi a un manipolo dentale.
Come vediamo le definizioni identificano tre dispositivi diversi, quattro con la fresa: non un insieme di essi già connessi uno all’altro.
2. TERMS AND DEFINITIONS
The EN ISO 1942: 2020 "Dentistry - Vocabulary" standard defines:
-Micromotor (micromotor): small motor used to power dental handpieces via direct connection;
-Dental handpiece: handle instrument used in dentistry for use in patient treatment;
-Air turbine or air turbin: high-speed pneumatic rotor used as the propulsion unit of a dental handpiece. In fact, it is also a single handpiece which, instead of working by mechanical ratio, works through a flow of air.
The definition of bur helps to definitively understand the function of the handpiece:
-Bur: rotary cutting tool consisting of head, neck and shank, designed to fit a dental handpiece.
As we can see, the definitions identify three different devices, four with the bur: and not a set of them already connected to each other.
3.IDENTIFICAZIONE DEI DISPOSITIVI
3.1Manipoli per micromotore
I manipoli per micromotore sono di due tipi a contrangolo, dritti e dritti a testa inclinata.
3.1.1.Manipoli a contrangolo
Generalmente utilizzati in profilassi, conservativa e in chirurgica, a seconda dell’uso hanno diverse velocità.
Osservando i modelli maggiormente utilizzati vediamo che, anche se esistono manipoli con variatore di velocità, ci sono manipoli la cui velocità predeterminata è individuabile attraverso un anello colorato di codifica.
3. IDENTIFICATION OF DEVICES
3.1 Handpieces for micromotor
There are two types of contra-angle handpieces for micromotors, straight and straight with
an inclined head.
3.1.1. Contra-angle handpieces
Generally used in prophylaxis, conservative and surgical, depending on the use they have
different speeds.
Observing the most used models we see that, even if there are handpieces with speed variator, there are handpieces whose predetermined speed can be identified through a colored coding ring.
In chirurgia, ad esempio in implantologia, si utilizza un manipolo che permette di collegare
dall’esterno soluzioni da erogare sulla fresa.
In surgery, for example in implantology, a handpiece is used that allows you to connect
solutions to be dispensed on the drill from the outside.
Es. di manipolo con irrigazione esterna
E.g. of handpiece with external irrigation
I manipoli possono avere anche una luce led.
The handpieces can also have an LED light.
Es. di manipolo con luce led
E.g. of a handpiece with LED light
E.g. of a handpiece with LED light
Si segnala anche la presenza di manipoli contrangolo dove è solo la testa che ha un’inclinazione rispetto al manico per permettere di raggiungere più facilmente l’area dei
molari.
We also point out the presence of contra-angle handpieces where only the head has an inclination with respect to the handle to allow easier access to the molar area.
molari.
We also point out the presence of contra-angle handpieces where only the head has an inclination with respect to the handle to allow easier access to the molar area.
Es. di manipolo dritto con testina angolata e 45°
E.g. of straight handpiece with angled and 45 ° head
E.g. of straight handpiece with angled and 45 ° head
3.1.2.Manipoli dritti
I manipoli dritti vengono impiegati quasi esclusivamente per i ritocchi, da effettuare direttamente nello studio odontoiatrico, sulle protesi.
Questo manipolo trasmette gli stessi giri del motore.
3.1.2.Straight handpieces
Straight handpieces are used almost exclusively for retouching, to be carried out directly in the dental office, on prostheses.
This handpiece transmits the same motor revolution
I manipoli dritti vengono impiegati quasi esclusivamente per i ritocchi, da effettuare direttamente nello studio odontoiatrico, sulle protesi.
Questo manipolo trasmette gli stessi giri del motore.
3.1.2.Straight handpieces
Straight handpieces are used almost exclusively for retouching, to be carried out directly in the dental office, on prostheses.
This handpiece transmits the same motor revolution
Es. di manipolo dritto
E.g. Of straight handpiece
E.g. Of straight handpiece
3.1.3.Trasmissione
La trasmissione di rotazione della testa avviene per mezzo di un moltiplicatore meccanico del manipolo alla fresa.
3.1.3 Transmission
The rotation transmission of the head takes place by means of a mechanical multiplier of the handpiece to the bur.
La trasmissione di rotazione della testa avviene per mezzo di un moltiplicatore meccanico del manipolo alla fresa.
3.1.3 Transmission
The rotation transmission of the head takes place by means of a mechanical multiplier of the handpiece to the bur.
4.MICROMOTORE
Il micromotore è un “micro” motore che eroga una velocita di circa 40.000 RPM giri al minuto (RPM – Revolution Per Minute - giri al minuto). Viene chiamato “micro” perché le use dimensioni sono particolarmente ridotte.
4.MICROMOTOR
The micromotor is a “micro” motor that delivers a speed of about 40,000 RPM revolutions per minute (RPM - Revolution Per Minute - revolutions per minute). It is called "micro" because the use dimensions are particularly small.
Il micromotore è un “micro” motore che eroga una velocita di circa 40.000 RPM giri al minuto (RPM – Revolution Per Minute - giri al minuto). Viene chiamato “micro” perché le use dimensioni sono particolarmente ridotte.
4.MICROMOTOR
The micromotor is a “micro” motor that delivers a speed of about 40,000 RPM revolutions per minute (RPM - Revolution Per Minute - revolutions per minute). It is called "micro" because the use dimensions are particularly small.
Es. di micromotore elettrico
E.g. of electric micromotor
E.g. of electric micromotor
Es. di micromotore elettrico (giri con gamma generalmente compresa fra 5.000 e 20.000)
E.g. of electric micromotor (revolutions with range generally between 5,000 and 20,000)
E.g. of electric micromotor (revolutions with range generally between 5,000 and 20,000)
Es. di micromotore con illuminazione led da trasmettere al manipolo
E.g. of micromotor with LED lighting to be transmitted to the handpiece
E.g. of micromotor with LED lighting to be transmitted to the handpiece
4.1.MECCANISMO DI FUNZIONAMENTO DEL MICROMOTORE
Sul mercato abbiamo due tipologie di micromotori, i micromotori BRUSH e BRUSHLESS che si differiscono per le diverse modalità di funzionamento.
4.1.MICROMOTOR OPERATING MECHANISM
We have two types of micromotors on the market, the BRUSH and BRUSHLESS micromotors which differ in the different operating modes.
Sul mercato abbiamo due tipologie di micromotori, i micromotori BRUSH e BRUSHLESS che si differiscono per le diverse modalità di funzionamento.
4.1.MICROMOTOR OPERATING MECHANISM
We have two types of micromotors on the market, the BRUSH and BRUSHLESS micromotors which differ in the different operating modes.
4.1.1.Micromotore Brush (micromotore a carboncini)
Si tratta di un sistema composto da uno statore al quale sono attaccati dei magneti permanenti, un rotore, sul quale sono posti delle piastre, un collettore (in rame) e 2 spazzole di carbone.
Il micromotore a spazzole può arrivare a compiere fino a 40.000 giri al minuto.
Le spazzole in carbonio vengono caricate elettricamente, hanno il compito di elettrificare meccanicamente le piastre presenti sul rotore, attraverso un contatto diretto con il collettore, questo moto meccanico permette la variazione dell’elettrificazione delle piastre in modo che vengano attratte dai magneti nello statore e permettere quindi la rotazione.
4.1.1. Brush micromotor (charcoal micromotor)
It is a system composed of a stator to which permanent magnets are attached, a rotor on which plates are placed, a collector (in copper) and 2 carbon brushes.
The brush micromotor can reach up to 40,000 revolutions per minute.
The carbon brushes are electrically charged, they have the task of mechanically electrifying the plates on the rotor, through direct contact with the collector, this mechanical motion allows the variation of the electrification of the plates so that they are attracted by the magnets in the stator and allow hence the rotation.
Mechanism of the carbon brush
Alcune tipologie di carboncini del micromotore
Some types of micro-motor charcoals
4.1.2.Micromotore Brushless (micromotore a induzione)
È costituito da un rotore e uno statore.
I micromotori ad induzione vengono azionati e controllati da un circuito ESC (Electronic Speed Control) così che la potenza venga regolata automaticamente, adattandosi immediatamente alla variazione delle sollecitazioni.
Il micromotore brushless può raggiungere una velocità fino a 50.000 rpm, è silenzioso, senza vibrazioni e molto leggero.
4.1.2.Brushless micromotor (induction micromotor)
It consists of a rotor and a stator.
The induction micromotors are driven and controlled by an ESC (Electronic Speed Control) circuit so that the power is automatically adjusted, adapting immediately to the variation in stress.
The brushless micromotor can reach speeds of up to 50,000 rpm, is quiet, vibration-free and very light.
È costituito da un rotore e uno statore.
I micromotori ad induzione vengono azionati e controllati da un circuito ESC (Electronic Speed Control) così che la potenza venga regolata automaticamente, adattandosi immediatamente alla variazione delle sollecitazioni.
Il micromotore brushless può raggiungere una velocità fino a 50.000 rpm, è silenzioso, senza vibrazioni e molto leggero.
4.1.2.Brushless micromotor (induction micromotor)
It consists of a rotor and a stator.
The induction micromotors are driven and controlled by an ESC (Electronic Speed Control) circuit so that the power is automatically adjusted, adapting immediately to the variation in stress.
The brushless micromotor can reach speeds of up to 50,000 rpm, is quiet, vibration-free and very light.
5.CORDONE DI ALIMENTAZIONE
Il cordone è il mezzo di collegamento fra micromotore e l’apparecchio di lavoro, come ad esempio il riunito o la consolle per chirurgia.
I cordoni possono permettere anche il passaggio dell’acqua (per spray sulla testa) oltre che dell’aria.
Il cordone non lo si indica quindi con il termine “cavo”, termine generalmente riservato al settore elettrico ovvero di sola alimentazione elettrica, al limite possiamo parlare di “cordone elettrificato”.
Ogni cordone, ovvero ogni micromotore, può avere attacchi diversi a seconda della tipologia di micromotore o di cordone.
Esistono anche cordoni polivalenti ai quali si può collegare, a scelta, sia il manipolo per turbina sia il manipolo per micromotore.
5. POWER CORD
The cord is the means of connection between the micromotor and the work device such as the dental unit or the surgery console.
The cords can also allow the passage of water (for spray on the head) as well as air.
The cord is therefore not indicated with the term "cable", a term generally reserved for the electrical sector or only for electrical power supply, in the limit we can speak of "electrified cord".
Each cord, or each micromotor, can have different connections depending on the type of micromotor or cord.
There are also multipurpose hoses to which both the turbine handpiece and the micromotor handpiece can be connected.
Il cordone è il mezzo di collegamento fra micromotore e l’apparecchio di lavoro, come ad esempio il riunito o la consolle per chirurgia.
I cordoni possono permettere anche il passaggio dell’acqua (per spray sulla testa) oltre che dell’aria.
Il cordone non lo si indica quindi con il termine “cavo”, termine generalmente riservato al settore elettrico ovvero di sola alimentazione elettrica, al limite possiamo parlare di “cordone elettrificato”.
Ogni cordone, ovvero ogni micromotore, può avere attacchi diversi a seconda della tipologia di micromotore o di cordone.
Esistono anche cordoni polivalenti ai quali si può collegare, a scelta, sia il manipolo per turbina sia il manipolo per micromotore.
5. POWER CORD
The cord is the means of connection between the micromotor and the work device such as the dental unit or the surgery console.
The cords can also allow the passage of water (for spray on the head) as well as air.
The cord is therefore not indicated with the term "cable", a term generally reserved for the electrical sector or only for electrical power supply, in the limit we can speak of "electrified cord".
Each cord, or each micromotor, can have different connections depending on the type of micromotor or cord.
There are also multipurpose hoses to which both the turbine handpiece and the micromotor handpiece can be connected.
Es. di cordone con passaggio di acqua
E.g. of a cord with the passage of water
E.g. of a cord with the passage of water
Es. di cordone polivalente
E.g. of polyvalent cord
E.g. of polyvalent cord
6.COLLEGAMENTO
Il micromotore sta in mezzo al manipolo e l’attacco del cordone è cioè il dispositivo che permette all’apparecchiatura e al manipolo di poter lavorare insieme.
6.LINK
The micromotor is in the middle of the handpiece and the cord attachment is the device that allows the equipment and the handpiece to work together.
Il micromotore sta in mezzo al manipolo e l’attacco del cordone è cioè il dispositivo che permette all’apparecchiatura e al manipolo di poter lavorare insieme.
6.LINK
The micromotor is in the middle of the handpiece and the cord attachment is the device that allows the equipment and the handpiece to work together.
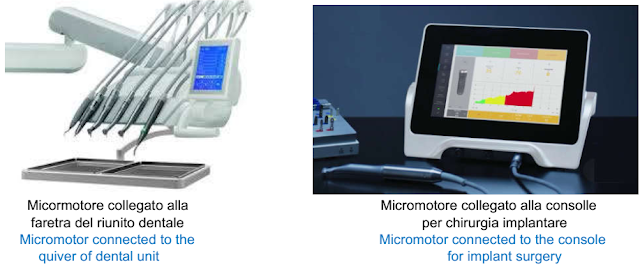
6.1.Lato apparecchiatura
Il lato apparecchio è quello che collega il micromotore, ad esempio, al riunito dentale o alla consolle per la chirurgia.
6.1.Equipment side
The device side is the one that connects the micromotor, for example, to the dental unit or to the surgery console
Il lato apparecchio è quello che collega il micromotore, ad esempio, al riunito dentale o alla consolle per la chirurgia.
6.1.Equipment side
The device side is the one that connects the micromotor, for example, to the dental unit or to the surgery console
6.2.Lato manipolo
Il lato manipolo è la parte del micromotore costituita dall’attacco del micromotore che permette al manipolo di eseguire le rotazioni che faranno girare la fresa inserita su di esso.
6.2 Handpiece side
The handpiece side is the part of the micromotor consisting of the attachment of the micromotor that allows the handpiece to perform the rotations that will make the cutter inserted on it turn.
Il lato manipolo è la parte del micromotore costituita dall’attacco del micromotore che permette al manipolo di eseguire le rotazioni che faranno girare la fresa inserita su di esso.
6.2 Handpiece side
The handpiece side is the part of the micromotor consisting of the attachment of the micromotor that allows the handpiece to perform the rotations that will make the cutter inserted on it turn.
che a sua volta è collegato all’apparecchio per chirurgia implantare.
Example of handpiece (A) inserted on the micromotor (B)
which in turn is connected to the implant surgery device.
Example of handpiece (A) inserted on the micromotor (B)
which in turn is connected to the implant surgery device.
7.ALTRI MANIPOLI
In odontoiatria i dispositivi coma la turbina, l’ablatore, gli strumenti piezoelettrici per chirurgia ecc. per il loro funzionamento sono collegati direttamente al cordone che a sua volta è collegato all’apparecchiatura in quanto non sono alimentati da un micromotore o altro dispositivo interconnesso. Anche questi dispositivi terminali prendono il nome di manipolo.
In odontoiatria i dispositivi coma la turbina, l’ablatore, gli strumenti piezoelettrici per chirurgia ecc. per il loro funzionamento sono collegati direttamente al cordone che a sua volta è collegato all’apparecchiatura in quanto non sono alimentati da un micromotore o altro dispositivo interconnesso. Anche questi dispositivi terminali prendono il nome di manipolo.
Per quanto riguarda la “turbina” c’è da dire che il termine si riferisce in realtà al rotore contenuto nel manipolo tanto è vero che la norma EN ISO 1942:2020 “Dentistry – Vocabulary” definisce come turbina (o rotore ad aria) il “rotore pneumatico ad alta velocità utilizzato come unità propulsiva di un manipolo odontoiatrico”.
7.OTHER HANDPIECES
In dentistry, devices such as turbine, scaler, piezoelectric instruments for surgery, etc. for their operation are connected directly to the cord which in turn is connected to the equipment as they are not powered by a micromotor or other interconnected devices. These terminal devices are also called a handpiece.
As for the "turbine" it must be said that the term actually refers to the rotor contained in the handpiece so much so that the EN ISO 1942: 2020 "Dentistry - Vocabulary" standard defines the turbine (or air rotor) as "High speed pneumatic rotor used as the propulsion unit of a dental handpiece".
Es. manipolo odontoiatrico con turbina comunemente chiamato turbina.
E.g. dental handpiece with turbine commonly called turbine.
E.g. dental handpiece with turbine commonly called turbine.
Es. di manipolo ultrasuoni per tartaro
E.g. of ultrasonic handpiece for tartar
E.g. of ultrasonic handpiece for tartar
8.CONCLUSIONI
-Il manipolo dentale (dental handpiece) è uno strumento con impugnatura utilizzato in odontoiatria per l'uso nel trattamento del paziente.
-Il micromotore (micromotor) è un piccolo motore utilizzato per alimentare i manipoli dentali tramite collegamento diretto con essi.
-Il micromotore per odontoiatria è quindi un dispositivo che, collegato mediante cordone all’apparecchiatura odontoiatrica, permette al manipolo di far ruotare la fresa dentale che viene inserita su di esso.
-Tutti gli strumenti con impugnatura collegati a una turbina, a un’ultrasuoni per tartaro, o a un generatore per la chirurgia piezoelettrica, e che permettono l’inserimento di punte, si chiamano manipoli.
-Il cordone è il dispositivo che collega il manipolo alla fonte di aria, acqua, elettricità ecc.
8.CONCLUSIONS
-The dental handpiece is a handpiece instrument used in dentistry for use in patient treatment.
-The micromotor is a small motor used to power the dental handpieces by direct connection with them.
-The micromotor for dentistry is therefore a device which, connected by cord to the dental equipment, allows the handpiece to rotate the dental bur that is inserted on it.
- All hand pieces connected to a turbine, to an ultrasound for tartar, or to a generator for piezoelectric surgery, and which allow the insertion of tips, are called handpieces.
-The cord is the device which connects the handpiece to the air source, water, electricity and so on.
-Il manipolo dentale (dental handpiece) è uno strumento con impugnatura utilizzato in odontoiatria per l'uso nel trattamento del paziente.
-Il micromotore (micromotor) è un piccolo motore utilizzato per alimentare i manipoli dentali tramite collegamento diretto con essi.
-Il micromotore per odontoiatria è quindi un dispositivo che, collegato mediante cordone all’apparecchiatura odontoiatrica, permette al manipolo di far ruotare la fresa dentale che viene inserita su di esso.
-Tutti gli strumenti con impugnatura collegati a una turbina, a un’ultrasuoni per tartaro, o a un generatore per la chirurgia piezoelettrica, e che permettono l’inserimento di punte, si chiamano manipoli.
-Il cordone è il dispositivo che collega il manipolo alla fonte di aria, acqua, elettricità ecc.
8.CONCLUSIONS
-The dental handpiece is a handpiece instrument used in dentistry for use in patient treatment.
-The micromotor is a small motor used to power the dental handpieces by direct connection with them.
-The micromotor for dentistry is therefore a device which, connected by cord to the dental equipment, allows the handpiece to rotate the dental bur that is inserted on it.
- All hand pieces connected to a turbine, to an ultrasound for tartar, or to a generator for piezoelectric surgery, and which allow the insertion of tips, are called handpieces.
-The cord is the device which connects the handpiece to the air source, water, electricity and so on.
9.BIBLIOGRAFIA
1.Norma EN ISO 1942:2020 “Dentistry – Vocabulary”;
2.Dental handpieces – an update - Nazma Akuji, Shilpa Shah, Martin Ashley - Dental UpdateVol. 41, No. 10 General Dentistry - Published Online: 6 Jul 2017 https://doi.org/10.12968/denu.2014.41.10.900;
3.The KaVo Advantage - Your guide to KaVo innovations2017 KaVo Dental - KV00022/B8.17;
4.Scienze dei materiali dentali e Laboratorio - S. Recchia – A. De Benedetto – Lucisano Editore – 2013;
5.La mia esperienza di tirocinio – Sara Losardo – Relazione tirocinio formativo presso Assitec Verona - 2019.
9.BIBLIOGRAPHY
1.Norma EN ISO 1942:2020 “Dentistry – Vocabulary”;
2.Dental handpieces – an update - Nazma Akuji, Shilpa Shah, Martin Ashley - Dental UpdateVol. 41, No. 10 General Dentistry - Published Online: 6 Jul 2017 https://doi.org/10.12968/denu.2014.41.10.900;
3.The KaVo Advantage - Your guide to KaVo innovations2017 KaVo Dental - KV00022/B8.17;
4.Scienze dei materiali dentali e Laboratorio - S. Recchia – A. De Benedetto – Lucisano Editore – 2013;
5.La mia esperienza di tirocinio – Sara Losardo – Relazione tirocinio formativo presso Assitec Verona - 2019.
3.The KaVo Advantage - Your guide to KaVo innovations2017 KaVo Dental - KV00022/B8.17;
4.Scienze dei materiali dentali e Laboratorio - S. Recchia – A. De Benedetto – Lucisano Editore – 2013;
5.La mia esperienza di tirocinio – Sara Losardo – Relazione tirocinio formativo presso Assitec Verona - 2019.























Nessun commento:
Posta un commento
Nota. Solo i membri di questo blog possono postare un commento.